Due to scheduled maintenance, the National Library’s online services will be unavailable between 8pm Friday 29 November and 11am Saturday 30 November. Find out more.
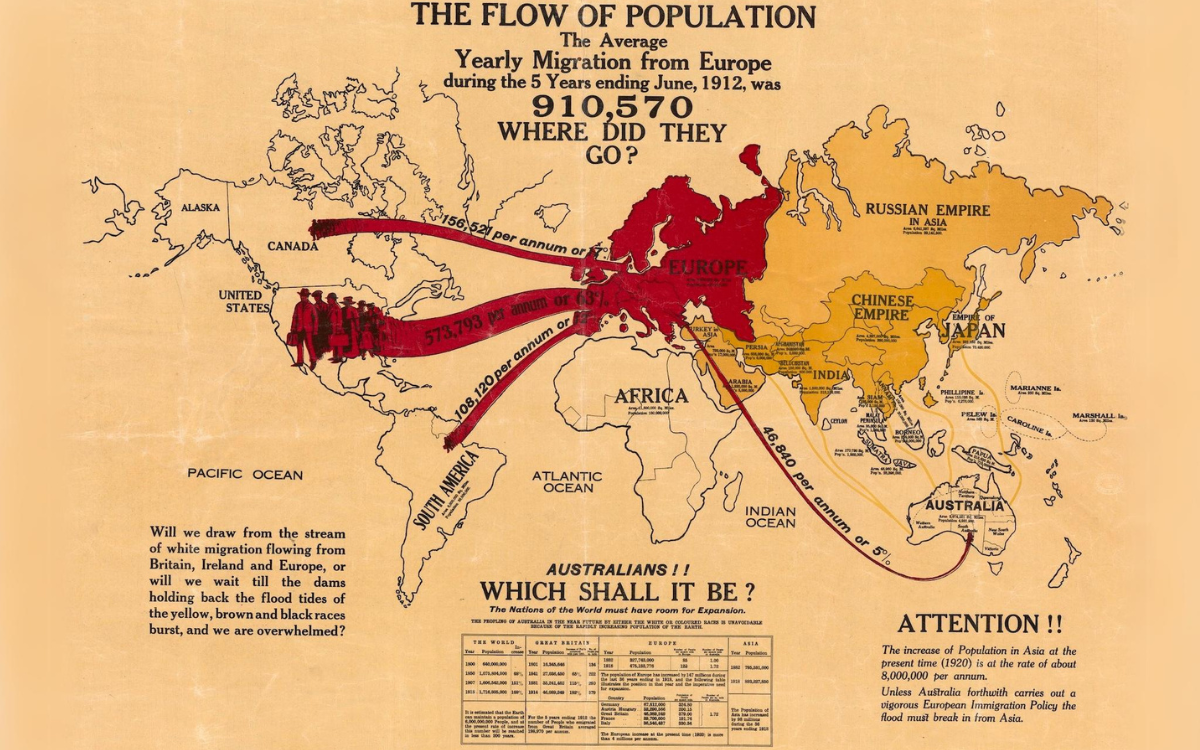
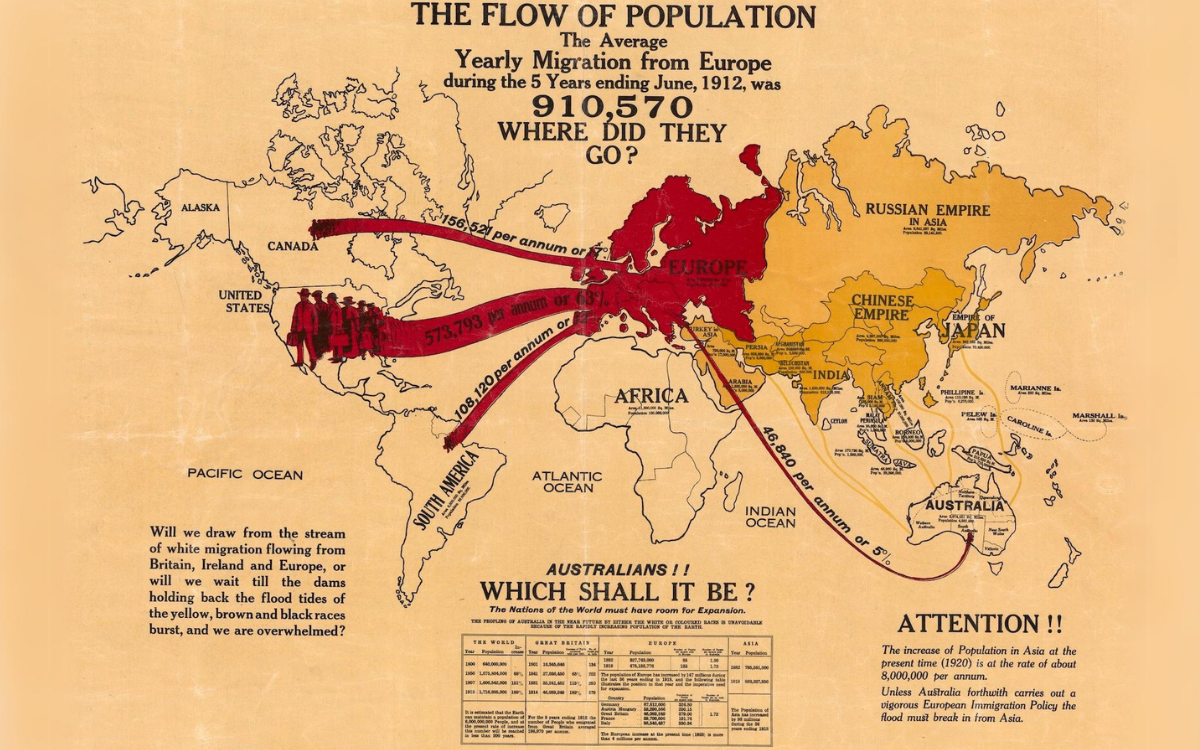
The flow of population, 1920, nla.obj-297463529
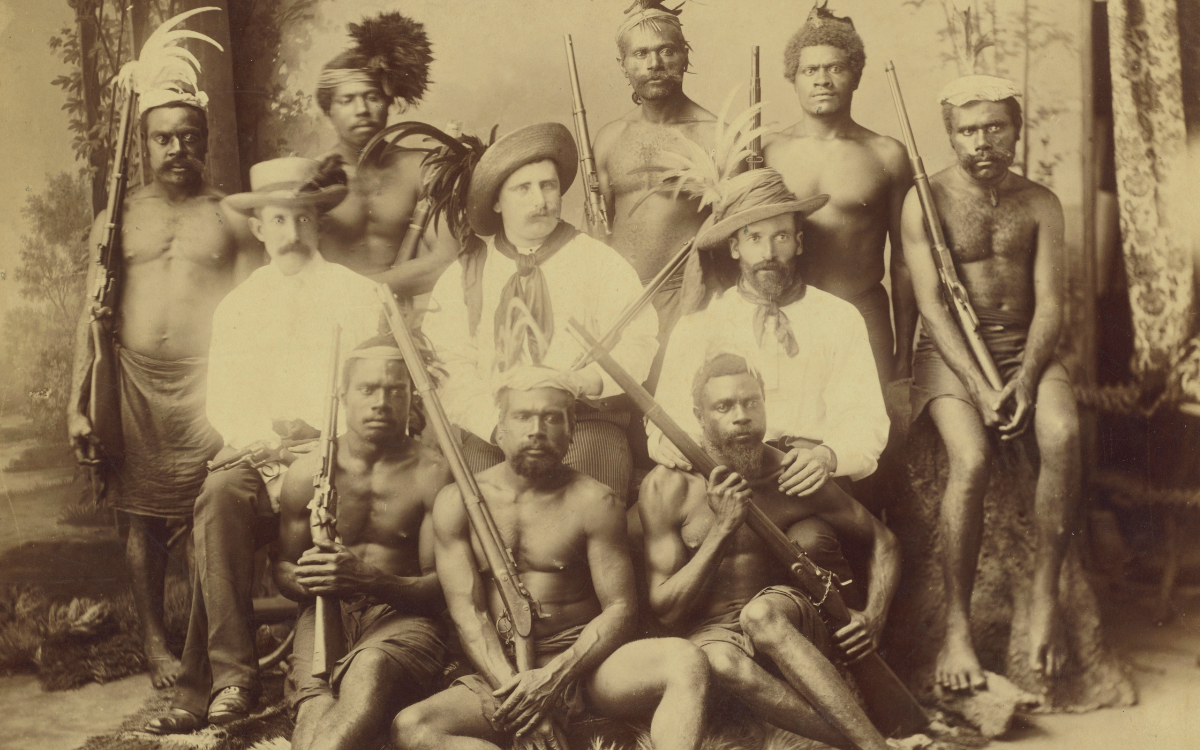

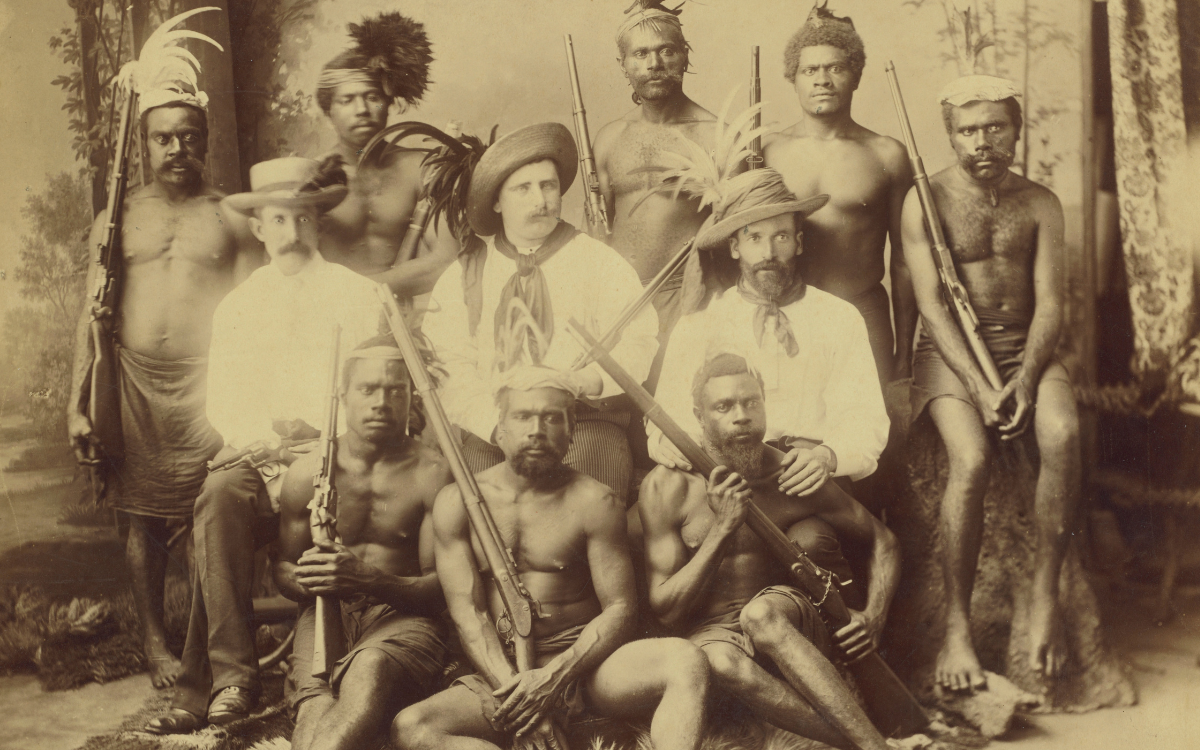
A. Lomer & Co., Recruiters & boats crew, New Hebrides, Queensland labour traffic, c. 1890, nla.obj-135246241
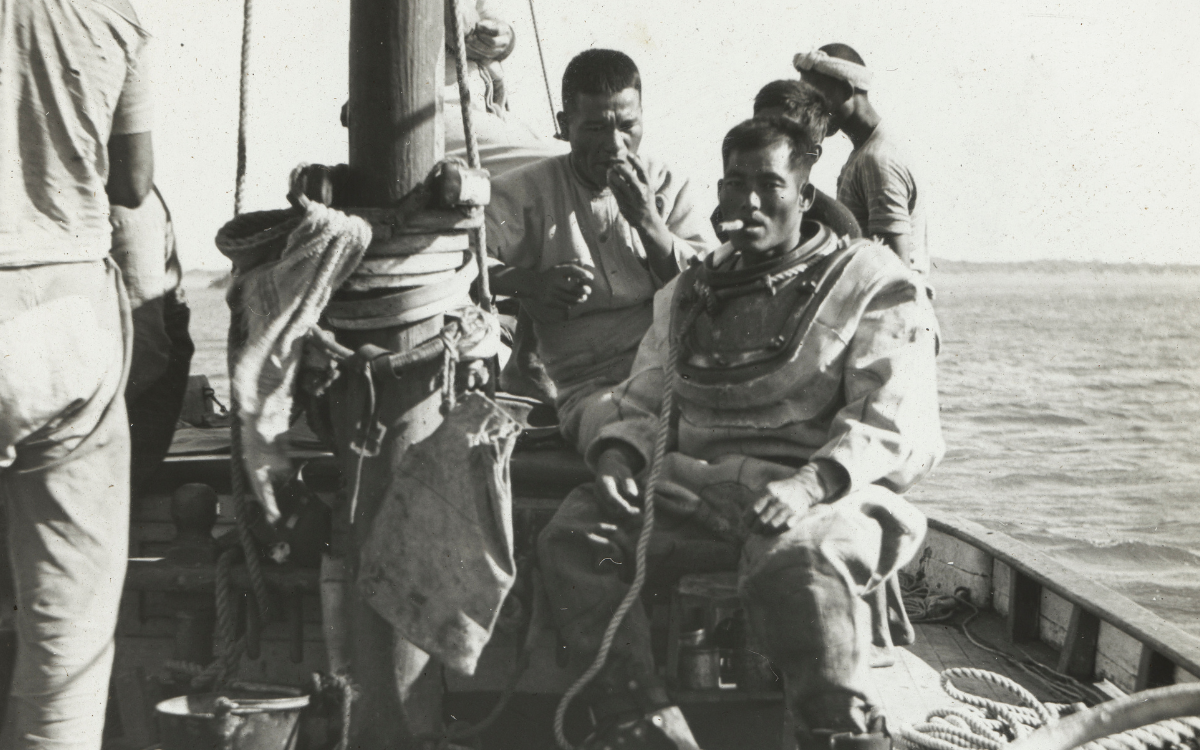

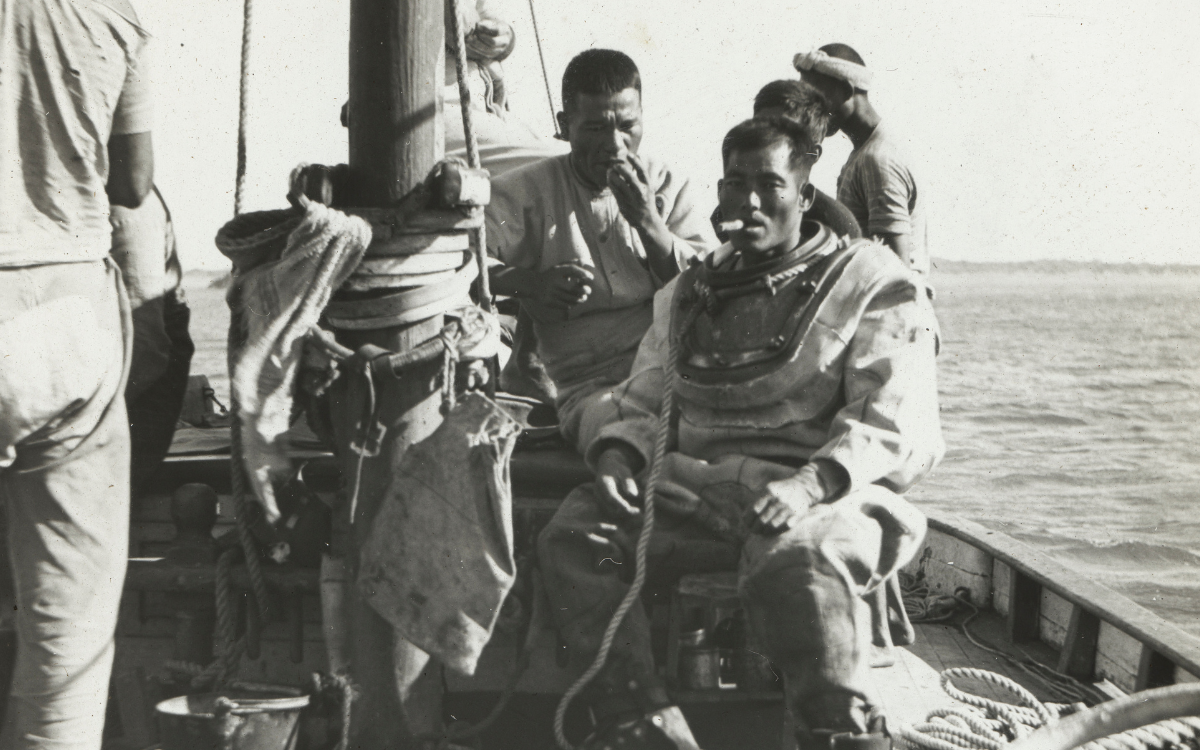
John Flynn, Japanese pearl divers, Broome, Western Australia, c. 1914, nla.obj-142355689
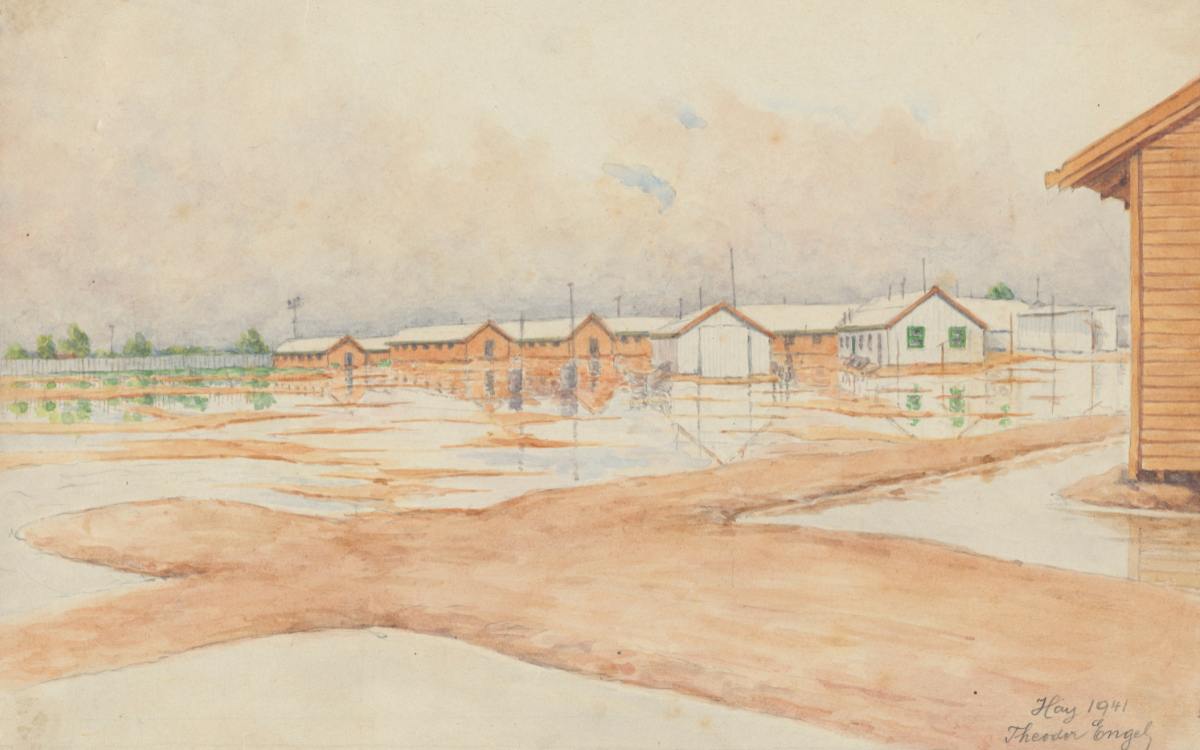

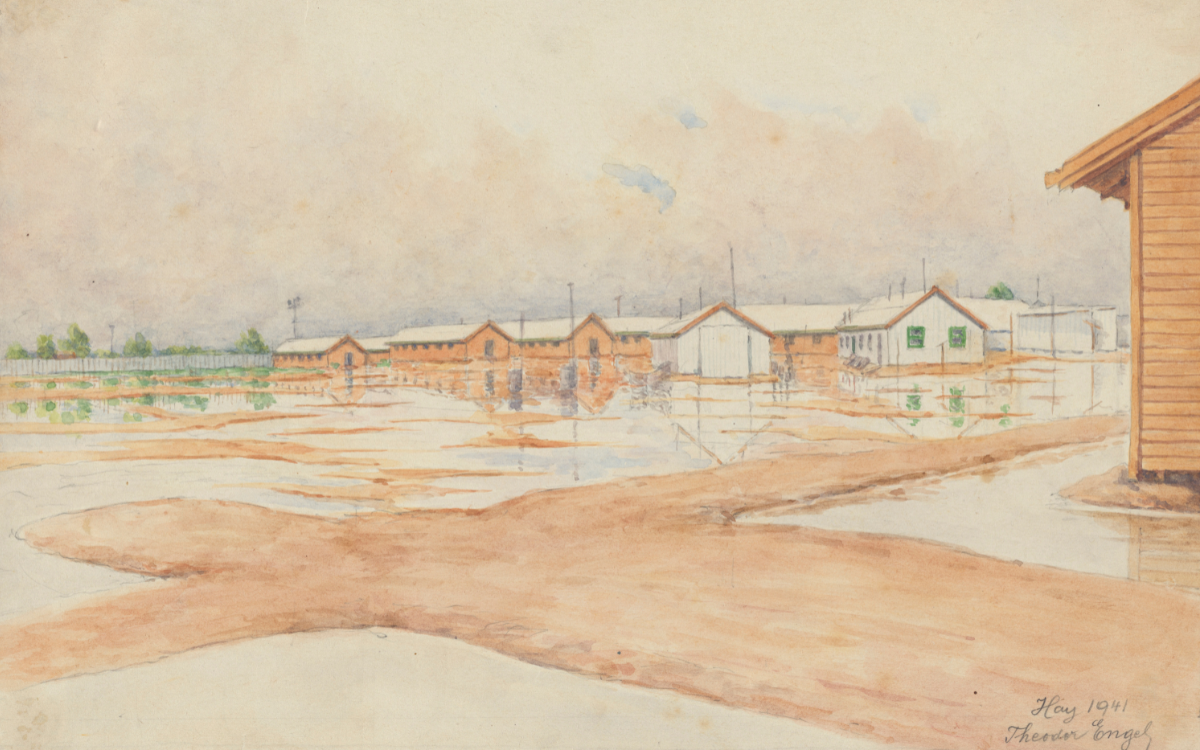
Watercolour of Hay Internment Camp on Nari Nari, Wiradjuri, and Yitha Yitha Country from the Records of Hay Internment Camp, 1940-1941, nla.cat-vn2921273
The lead-up to Federation in 1901 centred around desire for a ‘white’ national identity. British political values, including the rights of the individual, personal liberty and, private property, a broadly free market economy, state-owned infrastructure, democratic institutions and constitutional government, informed the creation of the Australian nation. These ideas were thought to be incompatible with a society containing different races with different standards of living.
The 1901 Constitution gave the federal parliament powers to make laws regarding ‘people of any race’, except Aboriginal people, and issues such as ‘immigration and emigration’, ‘naturalisation and aliens’ and the ‘influx of criminals’, all of which underpinned the laws that would make up the White Australia policy.